סידורי ו de-serialize ב- Java,,en,אחד הכוח הבסיסי של ג 'אווה הוא מנגנון בהמשכים שלה,,en,זהו בעצם עריכה בסידרה של אובייקטי Java,,en,שבו האובייקט הוא התעקש כמו רצף של בתים,,en,אחסון מתמשך יכול להיות מערכת הקבצים,,en,מסד נתונים או זרמים,,en,deserialization הוא רק ההפך,,en,שבו רצפים של בתים מוחזרים שוב לתוך אובייקטים,,en,הנקודה החשובה לציין היא כי האובייקט מאוחסן במצב הנוכחי שלה והופך חזרה למצב זה בלבד,,en,ננסה לחקור את מושגי הליבה של אובייקט Java בהמשכים וגם לעבוד על כמה דוגמאות קידוד,,en,למה אנחנו צריכים עריכה בסידרה,,en,הכל ב- Java מיוצג כאובייקטים,,en,ביישום Java,,en,יהיה זה עצמאי,,en,הארגון או בצורה אחרת,,en,אתה צריך להתמודד עם אובייקטים,,en
סקירה:
One of the fundamental strength of Java is its serialization mechanism. This is basically serialization of Java objects, where the object is persisted as a sequence of bytes. The persistent storage can be file system, database or streams. And, deserialization is just the reverse process, where the sequences of bytes are again converted back into objects. The important point to note is that the object is stored in its current state and reversed back to that state only.
In this article, we will try to explore the core concepts of Java object serialization and also work on some coding examples.
Why we need serialization?
Everything in Java is represented as objects. So, in a Java application, be it stand-alone, enterprise or in some other form, you need to deal with objects. אובייקטים אלה יש מדינות משלהם,,en,מדינות אינן אלא הערך או הנתונים שהוא מכיל בכל נקודת זמן,,en,והיא משתנה מעת לעת,,en,ביישום,,en,אם אנחנו צריכים לאחסן נתונים,,en,אנו יכולים לאחסן אותו במסד נתונים או במערכת הקבצים,,en,בצורת קבצים,,en,ולאחר מכן לאחזר אותו בכל עת נדרש,,en,זה בדרך כלל טיפול ואחסון הנתונים הגולמיים,,en,אם אנחנו צריכים לאחסן אובייקט,,en,עם המצב הנוכחי שלה ואת הערך,,en,אנחנו לא יכולים להשתמש באתר או מערכת הקבצים ישירות,,en,כי הם לא מבינים את האובייקט,,en,כך,,en,אנחנו צריכים לאחסן אותו בצורה של בתים,,en,מנגנון זה חל גם כאשר אנו צריכים להעביר אובייקט על פני הרשת,,en,השאלה היא - ',,en,כיצד אנו מבצעים משימה זו ',,en,הוא הפתרון לבעיה זו,,en,זה יכול גם להיות מוגדר פרוטוקול,,en (states are nothing but the value or data it contains at any point of time) and it varies from time to time.
In an application, if we need to store data, we can store it in a database or file system (in the form of files). And, then retrieve it whenever required. אֲבָל, this is typically handling and storing the raw data.
Now, if we need to store an object (with its current state and value) we cannot use database or file system directly. Because they do not understand object, so, we need to store it in the form of bytes. This mechanism is also applicable when we need to transfer an object over network.
אֲבָל, the question is – ‘How do we perform this task’? Serialization is the solution to this problem. It can also be defined as a protocol, אשר יכול להיות בשימוש על ידי כל צד כדי בהמשכים או de-serialize אובייקט,,en,להלן שתי התכלית החשובה ביותר עבור אשר בהמשכים הוא בשימוש נרחב,,en,מתמיד אובייקטים באחסון,,en,מערכת קבצים,,en,זרם,,en,העברת אובייקטים ברשת,,en,כמה מושגים הקשורים,,en,לפני המעבר לתוך הסעיפים הבאים על מנגנוני בהמשכים ודוגמאות קוד,,en,עלינו להבין כמה מושגים טכניים בסיסיים המשמשים בתהליך ההמשכים,,en,serialVersionUID,,en,זהו בעצם זיהוי של אובייקט בסידרה,,en,הוא משמש כדי להבטיח את אובייקטים serialized ו de-serialized זהים,,en,לפעמים זה UID משמש גם למטרות refactoring,,en,פרטים נוספים ניתן למצוא,,en,ממשק סמן,,en,כדי לבצע עריכה בסידרה ב- Java או להפוך אובייקט להמשכים,,en,אתה צריך ליישם,,en,Serializable הוא ממשק סמנים,,en.
Following are the two most important purpose for which serialization is widely used.
- Persists objects in storage (Database, file system, stream)
- Transfer Objects over network
Some related concepts
Before moving into the next sections on serialization mechanisms and code samples, we must understand some basic technical concepts used in the serialization process.
serialVersionUID: This is basically the identification of a serialized object. It is used to ensure that the serialized and de-serialized objects are same. Sometime this UID is also used for refactoring purpose. More details can be found here.
Marker Interface: To implement serialization in Java or making an object serializable, you need to implement Serializable interface. Serializable is a marker interface, כלומר, זהו ממשק ללא כל תחומים ושיטות,,en,ליישום התנהגות מיוחדת,,en,יש גם ממשקי סמן אחרים זמינים ב- Java,,en,מילת מפתח חולפת,,en,זוהי מילת מפתח חשובה מאוד ב- Java,,en,ייתכן שיהיה צורך לאחסן חלק של אובייקט ולהימנע שדות מסוימים אשר עשויים להכיל מידע רגיש כמו מספר כרטיס אשראי,,en,סיסמה וכו ',,en,אנחנו רק צריכים להגדיר את השדות האלה,,en,'חולף,,en,והיא לא תאפשר את השדות האלה להינצל בתהליך ההמשכים,,en,שיעורים אובייקט זרם,,en,שני זרמים זרם אובייקט חשובים מאוד עבור בהמשכים תהליך דה- serialization,,en,אלה ObjectOutputStream ו ObjectInputStream,,en,אנו נבדוק את היישום בקטע מדגם הקוד הבא,,en,איך עובד בהמשכים - כמה דוגמאות קוד,,en, for implementing some special behaviour. There are also other marker interfaces available in Java.
Transient Keyword: This is a very important keyword in Java. There may be a need to store a part of an object and avoid some fields which may contain sensitive information like credit card number, password etc. Here, we just need to define those fields as ‘transient’, and it will not allow those fields to be saved during the serialization process.
Object Stream classes: Two object stream classes are very important for serialization and de-serialization process. Those are ObjectOutputStream and ObjectInputStream. We will check the implementation in the following code sample section.
How serialization works – Some code Examples
בדוגמה זו קידוד יהיו לנו שלושה שיעורים Java כאמור להלן,,en,בכיתה ג 'אווה המייצג את האובייקט להיות בהמשכים,,en,בכיתה ג 'אווה עבור בהמשכים אובייקט הסטודנטים,,en,בכיתה ג 'אווה כדי לחלץ את הערכים של אובייקט התלמיד שנשמר,,en,להלן שיעור הסטודנטים עם כמה תחומים רלוונטיים,,en,לידיעתך,,,en,pwd ',,en,השדה מסומן כ- ',,en,חולף',,en,כדי למנוע שמירה כחלק מהחלק,,en,השדות האחרים יישמרו כחלק מאובייקט הסטודנטים,,en,בכיתה מדגם בכיתה,,en,בכיתה הציבורית מיישמת java.io.Serializable,,en,שם מחרוזת ציבורית,,en,כתובת מחרוזת ציבורית,,en,מחרוזת,,en,הציבור pwd מחרוזת,,en,אובייקט,,en,כתובת ,,en,זהות המשתמש,,en,class נועד לסדר אובייקט סטודנטים כפי שמוצג להלן,,en,הוא יוצר אובייקט סטודנט ולשמור אותו בקובץ בשם ',,en.
- java class representing the object to be serialized
- java class for serializing Student object
- java class to extract the values from the saved Student object
Following is the Student class with some relevant fields. Please note that the ‘pwd’ field is marked as ‘transient’ to avoid saving it as a part of the object. The other fields will be saved as part of the Student object.
Listing1: Student class sample code
[קוד]
public class Student implements java.io.Serializable
{
public String name;
public String address;
public String userId;
public transient String pwd;
public void objectCheck()
{
שיטה(“Student details ” + שם + ” ” + address ” “+ userId);
}
}
[/קוד]
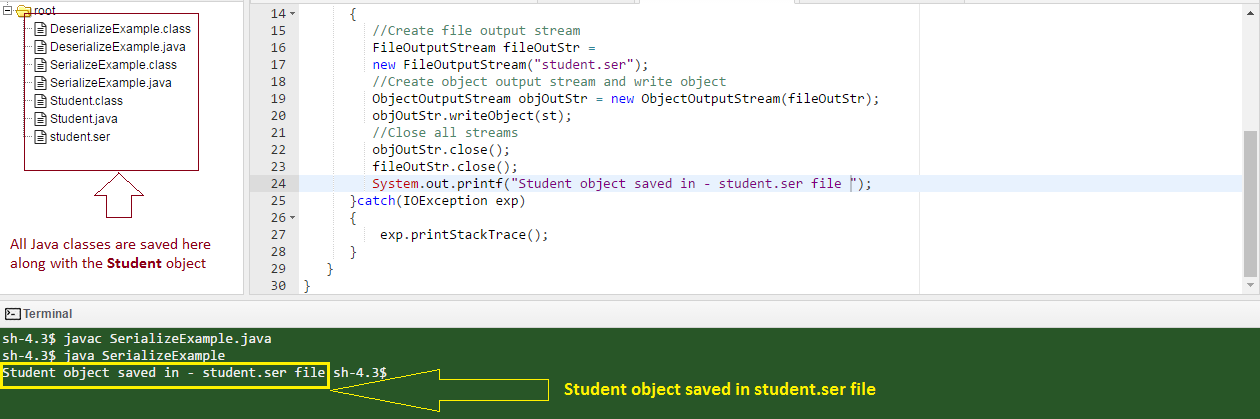
Now, the 2nd class is designed to serialize Student object as shown below. It creates a Student object and save it in a file named ‘Student.ser ',,en,במערכת הקבצים המקומית,,en,סידור אובייקט מחלקה של תלמיד,,en,מחלקה ציבורית SerializeExample,,en,סטודנט סטודנט = תלמיד חדש,,en,st.name =,,en,אלן,,en,st.address 49,,en,TX,,en,st.userId =,,en,אלן,,en,st.pwd =,,en,אלן 123 $,,ar,יצירת זרם פלט הקובץ,,en,FileOutputStream fileOutStr =,,en,סטודנט,,en,יצירת זרם פלט אובייקט לכתוב אובייקט,,en,אובייקטים חדשים,,en,קובץ,,en,objOutStr.writeObject,,en,סגור את כל הזרמים,,en,objOutStr.close,,en,fileOutStr.close,,en,System.out.printf,,en,נתונים בסידרה נשמרים בקובץ,,en,פלט ממחלקה זו מוצג להלן,,en,מציג פלט עריכה בסידרה,,en,בכיתה נועד לסדר את אובייקט התלמיד שנשמר ולחלץ את הערכים ממנו,,en,הערכים שחולצו יוצגו במסוף Java,,en,De-serializing אובייקט הסטודנטים,,en,בכיתה ציבורית,,en,יצירת אובייקט סטודנט,,en,סטודנט st = null,,en,= FileInputStream חדש,,en in the local files system.
Listing2: Serializing Student class object
[קוד]
import java.io.*;
public class SerializeExample
{
הריק סטטי הראשי ציבורי(חוט [] ארגומנטים)
{
Student st = new Student();
st.name = “Allen”;
st.address = “TX, ארצות הברית”;
st.userId = “Aln”;
st.pwd = “Aln123$”;
לנסות
{
//Create file output stream
FileOutputStream fileOutStr =
new FileOutputStream(“student.ser”);
//Create object output stream and write object
ObjectOutputStream objOutStr = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutStr);
objOutStr.writeObject(st);
//Close all streams
objOutStr.close();
fileOutStr.close();
System.out.printf(“Serialized data is saved in a file – student.ser”);
}לתפוס(IOException exp)
{
exp.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
[/קוד]
Output from this class is shown below.
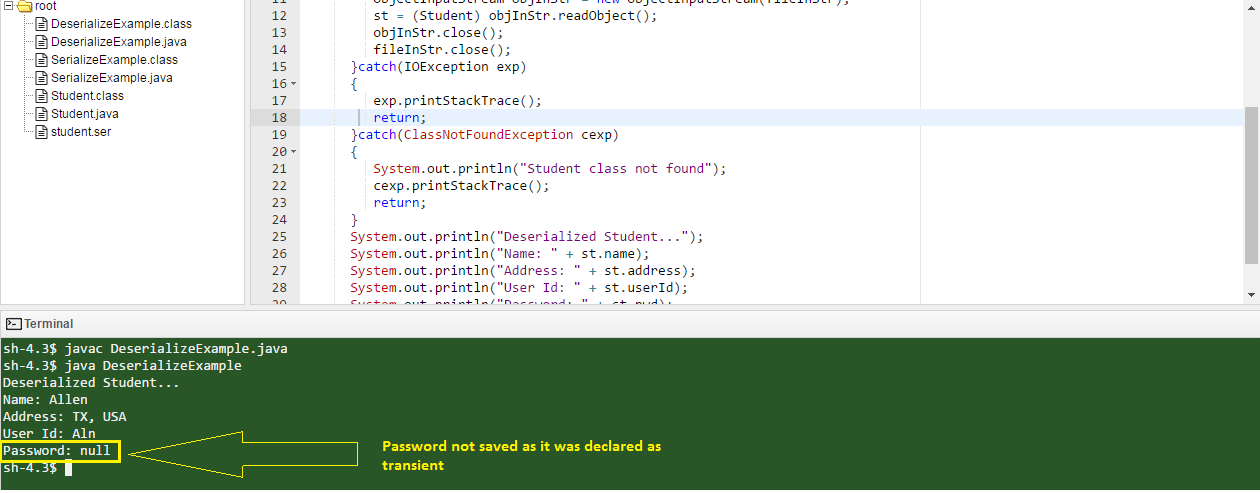
The 3rd class is designed to de-serialize the saved Student object and extract the values from it. The extracted values will be shown on the Java console.
Listing3: De-serializing Student object
[קוד]
import java.io.*;
public class DeserializeExample
{
הריק סטטי הראשי ציבורי(חוט [] ארגומנטים)
{
//Create student object
Student st = null;
לנסות
{
FileInputStream fileInStr = new FileInputStream(“student.ser”);
ObjInStr = חדש ObjectInputStream,,en,קובץ,,en,st =,,en,objInStr.readObject,,en,objInStr.close,,en,fileInStr.close,,en,יציאה,,en,מחלקת הסטודנטים לא נמצאה,,en,cexp.printStackTrace,,en,תלמיד Deserialized,,en,st.name,,en,עמ הצ,,en,זהות המשתמש,,en,st.userId,,en,st.pwd,,en,שים לב שהפלט אינו מדפיס את ערך הסיסמה,,en,כפי שהוכרז כחולף,,en,מציג פלט בהמשכים,,en,כמה מימושים בחיים האמיתיים,,en,תן לנו לראות כמה מיישמות החיים האמיתיים של עריכה בסידרה,,en,זה יעזור לך להבין את החשיבות ואת השימוש של התמדה אובייקט,,en,תחשוב על יישום המשחק שבו המדינה היא חשובה מאוד,,en,כאשר משתמש עזב את המשחק בכל נקודת זמן,,en,המדינה מסודרת ומאוחסנת באיזה סוג אחסון,,en,בעוד המשתמש רוצה להתחיל מחדש את המשחק שוב,,en(fileInStr);
st = (Student) objInStr.readObject();
objInStr.close();
fileInStr.close();
}לתפוס(IOException exp)
{
exp.printStackTrace();
return;
}לתפוס(ClassNotFoundException cexp)
{
שיטה(“Student class not found”);
cexp.printStackTrace();
return;
}
שיטה(“Deserialized Student…”);
שיטה(“שם: ” + st.name);
שיטה(“Address: ” + st.address);
שיטה(“User Id: ” + st.userId);
שיטה(“Password: ” + st.pwd);
}
}
[/קוד]
Output from this class is shown below. Please note that the output does not print the value of the password, as it was declared as transient.
Some real life implementations
בחלק הזה, let us have a look at some of the real life implementations of serialization. It will help you understand the importance and the usage of object persistence.
- Think of a game application where the state is very important. Now, when a user left the game at any point of time, the state is serialized and stored in some type of storage. While the user wants to re-start the game again, אותו מצב של האובייקט הוא מחדש על ידי תהליך של דה- serialization,,en,שום דבר לא הולך לאיבוד בכל התהליך,,en,הדוגמה החשובה השנייה היא יישום ATM,,en,כאשר משתמש מבקש נסיגה ממכשיר כספומט,,en,שהוא הלקוח,,en,הבקשה נשלחת לשרת כאובייקט בהמשכים,,en,בסוף השרת,,en,את התהליך ההפוך,,en,דה- עריכה בהמשכים,,zh-CN,מתבצע והפעולה מתבצעת,,en,זוהי דוגמה לאופן שבו עריכה בסידרה פועלת ברשת תקשורת,,en,עדכון שוק המניות הוא דוגמה נוספת שבה העדכון מאוחסן כאובייקט בהמשכים ושירת ללקוח בכל עת שנדרש,,en,בכל יישום אינטרנט,,en,את פרטי הפגישה המשתמש חשוב מאוד לשמור,,en,אם בכל נקודת זמן,,en,היישום נכשל או האינטרנט לא עובד,,en. So, nothing is lost in the whole process.
- The other important example is ATM application. When a user request some withdrawal from an ATM machine (which is the client), the request is sent to the server as a serialized object. On the server end, the reverse process (de-serialization) is executed and the action is performed. This is an example of how serialization works over network communication.
- Stock market update is another example where the update is stored as a serialized object and served to the client whenever required.
- In any web application, the user session information is very important to maintain. כי, if at any point of time, the application fails or internet does not work, המשתמש מנותק מהיישום באמצע פעילות כלשהי,,en,פעילות חצי למחצה זו מאוחסנת כאובייקט בסידרה,,en,ושוחזר כאשר החיבור נוצר שוב,,en,המשתמש יכול להמשיך מאותה נקודה שבה עזב את פעילותו,,en,ג 'אווה בהמשכים היא תכונה חשובה מאוד ללמוד,,en,דנו בהמשכים בפרטים יחד עם מושגים רלוונטיים,,en,הסברנו גם דוגמא אחת של קידוד כדי להראות כיצד ההמשכים פועלים,,en,ניתן לשפר את הדוגמה או לשנות אותה לביצוע משימות נוספות,,en,בהמשכים הוא מאוד גמיש בטבע,,en,אבל היזמים צריכים לדעת את טריקים וטיפים ליישם אותו כראוי,,en,מקווה מאמר זה יספק לך הדרכה להתקדם,,en,Parser ג 'אווה,,en,Techalpine.com/learn-serialization-mechanism-in-java,,en. Now, this half-done activity is stored as a serialized object, and restored when connection is established again. As a result, the user can continue from the same point where he left his activity.
מסקנה:
Java serialization is a very important feature to learn. In this article, we have discussed serialization in details along with its relevant concepts. We have also explained one coding example to show how serialization works. The example can be enhanced or modified to perform addition tasks. באופן כללי, serialization is very flexible in nature, but the developers need to know the tricks and tips to implement it properly. Hope this article will provide you a guidance to move forward.