10 Java Tips – ທ່ານຕ້ອງຮູ້,,en,ການຈັດການຫນ່ວຍຄວາມຈໍາໃນ Java,,en,ການໂຕ້ຕອບໄດ້ຖືກນໍາສະເຫນີເພື່ອຮັບໃຊ້ຈຸດປະສົງແລະມັນໄດ້ມາຈາກເປົ້າຫມາຍ C,,en,ເຫດຜົນສໍາລັບການຍົກເລີກມໍລະດົກຫຼາຍຈາກພາສາ Java ແມ່ນສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ແມ່ນມາຈາກ,,en,ເປັນພາສາງ່າຍດາຍ,,en,ຜູ້ສ້າງ Java ຕ້ອງການພາສາທີ່ນັກພັດທະນາສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ສາມາດເຂົ້າໃຈໄດ້ໂດຍບໍ່ມີການຝຶກອົບຮົມຢ່າງກວ້າງຂວາງ,,en,ໂດຍບໍ່ມີການດໍາເນີນການສັບຊ້ອນທີ່ບໍ່ຈໍາເປັນຂອງ C ,,en,ໃນການອອກແບບ,,en,ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ,,en,ຄວາມມໍລະດົກຫຼາຍເຮັດໃຫ້ບັນຫາຕ່າງໆແລະຄວາມສັບສົນຫຼາຍກວ່າມັນແກ້ໄຂ,,en,ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ພວກເຂົາໄດ້ຕັດສິນໃຈຫລາຍຈາກພາສາ,,en,ພຽງແຕ່ຍ້ອນວ່າພວກເຂົາຕັດຕົວຜູ້ບໍລິຫານເກີນໄປ,,en,ຜູ້ອອກແບບ,,en,ປະສົບການ C ຢ່າງກວ້າງຂວາງໄດ້ສອນໃຫ້ພວກເຂົາຮູ້ວ່າມໍລະດົກຫຼາຍໆຢ່າງບໍ່ໄດ້ເປັນຄວາມເຈັບປວດ,,en,ຜູ້ອອກແບບຂອງ Java ໄດ້ເລືອກທີ່ຈະອະນຸຍາດໃຫ້ມີການແບ່ງປັນຊັບສົມບັດຫຼາຍໂດຍຜ່ານການນໍາໃຊ້ອິນເຕີເຟດ,,en
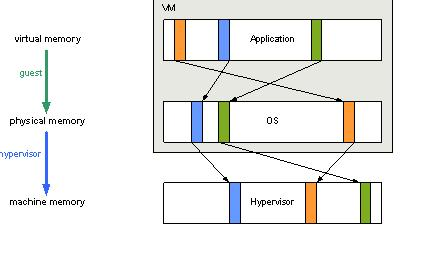
How memory is managed in java?
In Java manual memory allocation and de-allocation has been eliminated. Memory in Java is automatically garbage collected so you never have to worry about memory corruption. Java memory is managed by the memory model. The Java Memory model explains synchronization techniques to make sure data corruption does not take place. Synchronization can also help to avoid deadlocks between threads and run programs smoothly. The following diagram gives an overview on java memory management.
Are multiple inheritances possible in java?
No, multiple inheritance is not possible in java. Interface has been introduced to serve the purpose and it has been derived from Objective C.
The reasons for omitting multiple inheritances from the Java language mostly stem from the “ງ່າຍດາຍ, ຈຸດປະສົງ, ຮັດກຸມແລະຄຸ້ນເຄີຍ” ເປົ້າຫມາຍຂອງ. As a simple language, Java’s creators wanted a language that most developers could grasp without extensive training. ແລະທ້າຍທີ່ສຸດ, ພວກເຂົາເຈົ້າໄດ້ເຮັດວຽກທີ່ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ພາສາເປັນຄ້າຍຄືກັນກັບ C ທີ່ເປັນໄປໄດ້ (ຄຸ້ນເຄີຍ) without carrying over C ’s unnecessary complexity (ງ່າຍດາຍ).
In the designers’ opinion, multiple inheritance causes more problems and confusion than it solves. So they cut multiple inheritances from the language (just as they cut operator overloading). The designers’ extensive C experience taught them that multiple inheritances just weren’t worth the headache.
Instead, Java’s designers chose to allow multiple interface inheritance through the use of interfaces, ຄວາມຄິດທີ່ໄດ້ຢືມຈາກໂປໂຕຄອນ Objective C,,en,ມໍລະດົກການໂຕ້ຕອບຫຼາຍອະນຸຍາດໃຫ້ມີວັດຖຸທີ່ຈະສືບທອດລາຍເຊັນວິທີການທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນດ້ວຍການລະວັງວ່າວັດຖຸທີ່ສືບທອດຕ້ອງປະຕິບັດຕາມວິທີທີ່ໄດ້ຮັບການສືບທອດມານັ້ນ,,en,ສິ່ງທີ່ເປົ້າຫມາຍການອອກແບບສິບເອັດຂອງ java ແມ່ນຫຍັງ,,en,ຕໍ່ໄປນີ້ແມ່ນສິບເອັດເປົ້າຫມາຍການອອກແບບຂອງພາສາການຂຽນພາສາ java,,en,ນັກອອກແບບ Java ໄດ້ສໍາເລັດວຽກງານໂດຍການຮັກສາເປົ້າຫມາຍເຫຼົ່ານີ້ຢູ່ໃນໃຈ,,en,Object Oriented,,en,ຕີລາຄາ,,en,ຖືກແຈກຢາຍ,,en,Multithreaded,,en,ປອດໄພ,,en,Dynamic,,en,Architecture Neutral,,en,ເປັນຫຍັງ java ຖືກເອີ້ນວ່າແຈກຢາຍ,,en,Java ມີຫ້ອງສະຫມຸດກວ້າງຂວາງສໍາລັບການໂຕ້ຖຽງ TCP / IP ເຊັ່ນ HTTP ແລະ FTP,,en,ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຄໍາຮ້ອງສະຫມັກ Java ສາມາດເປີດແລະເຂົ້າເຖິງວັດຖຸທົ່ວອິນເຕີເນັດຜ່ານ URLs,,en,ໂປລແກລມເຄືອຂ່າຍການນໍາໃຊ້ java ແມ່ນເຂັ້ມແຂງແລະງ່າຍທີ່ຈະໃຊ້,,en,ດັ່ງນັ້ນ java ຖືກເອີ້ນວ່າແຈກຢາຍ,,en. Multiple interface inheritance allows an object to inherit many different method signatures with the caveat that the inheriting object must implement those inherited methods.
What are the eleven design goals of java?
Following are the eleven design goals of java programming language. Java designers have accomplished the task by keeping these goals in mind.
- Simple
- Portable
- Object Oriented
- Interpreted
- Distributed
- High Performance
- Robust
- Multithreaded
- Secure
- Dynamic
- Architecture Neutral
Why java is called distributed?
Java has an extensive library of routines for handling TCP/IP protocols like HTTP and FTP. So Java applications can open and access objects across the internet via URLs. The network programming using java is strong and easy to use. So java is called distributed.
ລັກສະນະທີ່ແຈກຢາຍຂອງ Java ກໍ່ຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໃນເວລາທີ່ສົມທົບກັບຄວາມສາມາດໃນການໂຫລດແບບເຄື່ອນໄຫວຂອງມັນ,,en,ຄຸນນະສົມບັດເຫຼົ່ານີ້ເຮັດໃຫ້ມັນເປັນໄປໄດ້ສໍາລັບນັກແປພາສາ Java ທີ່ຈະດາວໂຫລດແລະໃຊ້ລະຫັດຜ່ານຈາກອິນເຕີເນັດ,,en,ນີ້ແມ່ນສິ່ງທີ່ເກີດຂື້ນໃນເວລາທີ່ເວັບເບົາເຊີດາວໂຫລດແລະຈັດການ applet Java,,en,ສະຖານະການສາມາດສັບສົນກວ່ານີ້,,en,ຈິນຕະນາການລະບົບປະຕິບັດການສື່ມວນຊົນຫຼາຍສື່ທີ່ຂຽນໄວ້ໃນ Java,,en,ເມື່ອໂຄງການນີ້ຖືກຂໍໃຫ້ສະແດງຂໍ້ມູນບາງຊະນິດທີ່ມັນບໍ່ເຄີຍພົບກ່ອນ,,en,ມັນອາດຈະສາມາດດາວໂຫຼດຊັ້ນຮຽນຈາກເຄືອຂ່າຍທີ່ສາມາດແຍກຂໍ້ມູນໄດ້,,en,ແລະຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນແບບເຄື່ອນໄຫວດາວໂຫລດຊັ້ນຮຽນອື່ນ,,en,ອາດຈະເປັນ Java,,en,ທີ່ສາມາດສະແດງຂໍ້ມູນພາຍໃນເອກະສານປະສົມ,,en,ໂຄງການເຊັ່ນນີ້ໃຊ້ຊັບພະຍາກອນກະຈາຍຢູ່ໃນເຄືອຂ່າຍເພື່ອການເຕີບໃຫຍ່ແລະປັບຕົວຕາມຄວາມຕ້ອງການຂອງຜູ້ໃຊ້,,en. Together, these features make it possible for a Java interpreter to download and run code from across the Internet. This is what happens when a Web browser downloads and runs a Java applet, ສໍາລັບຕົວຢ່າງ. Scenarios can be more complicated than this, however. Imagine a multi-media word processor written in Java. When this program is asked to display some type of data that it has never encountered before, it might dynamically download a class from the network that can parse the data, and then dynamically download another class (probably a Java “bean”) that can display the data within a compound document. A program like this uses distributed resources on the network to dynamically grow and adapt to the needs of its user.
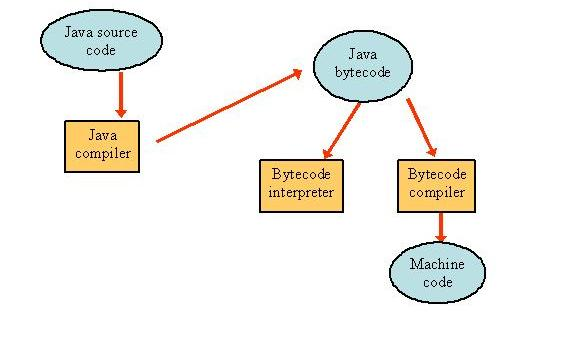
ເປັນຫຍັງ java ເອີ້ນວ່າຖາປັດຕະຍະທີ່ເປັນກາງ,,en,ຕົວປະສານງານ Java ສ້າງຄໍາສັ່ງ bytecode ເຊິ່ງເປັນເອກະລາດຂອງສະຖາປັດຕະຍະກໍາຄອມພິວເຕີ,,en,bytecode ຖືກອອກແບບມາເພື່ອໃຫ້ງ່າຍຕໍ່ການຕີຄວາມກ່ຽວກັບເຄື່ອງໃດກໍ່ໄດ້ແລະແປໄດ້ງ່າຍໃນລະຫັດເຄື່ອງຂອງເຄື່ອງທໍາມະຊາດ,,en,ແຜນທີ່ດັ່ງຕໍ່ໄປນີ້ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນລາຍລະອຽດຂອງວິທີການເຮັດວຽກ,,en,Java architecture neutral,,en,ເປັນຫຍັງ browser java ເປີດໃຊ້ງານຈຶ່ງຈໍາເປັນຕ້ອງໃຊ້ applet,,en,Applet ແມ່ນໂຄງການ java ທີ່ເຮັດວຽກຢູ່ຫນ້າເວັບ,,en,ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຕົວທ່ອງເວັບຄວນມີຄວາມສາມາດທີ່ຈະຕີຄວາມຫມາຍ bytecode ແລະເຮັດໃຫ້ມັນເຮັດວຽກ,,en,ນັ້ນແມ່ນເຫດຜົນທີ່ວ່າຕົວທ່ອງເວັບທີ່ເປີດໃຊ້ java ແມ່ນຕ້ອງໃຊ້ applet ທີ່ຖືກຝັງໄວ້ໃນຫນ້າເວັບ,,en,ຕົວຈິງແລ້ວ, ຕົວທ່ອງເວັບມີ JVM inbuilt ເຊິ່ງຊ່ວຍໃຫ້ຕີຄວາມຫມາຍລະຫັດ byte ແລະສະແດງຜົນອອກ,,en?
The Java compiler generates a bytecode instruction which is independent of computer architecture. The bytecode is designed to be both easy to interpret on any machine and easily translated into native machine code on the fly. The following diagram shows the details how it works.
Why java enabled browser is needed to run an applet?
Applet is a java program that works on a web page. So the browser should have the capability to interpret the bytecode and make it work. That is why java enabled browser is required to run an applet embedded in a web page. Actually the browser contains the JVM inbuilt which helps to interpret the byte code and show the output.
ທ່ານຫມາຍຄວາມວ່າແນວໃດໂດຍ "Java ແມ່ນພາສາທີ່ຖືກພິມຢ່າງແຂງແຮງ",,en,Java ແມ່ນພິມຢ່າງເຂັ້ມງວດຫມາຍຄວາມວ່າທຸກໆຕົວໃນ java ຕ້ອງມີປະເພດປະກາດ,,en,ມີແປດປະເພດທໍາອິດໃນ Java,,en,ສີ່ຂອງພວກມັນແມ່ນປະເພດ integer ແລະສອງແມ່ນປະເພດຈໍານວນ floating ຈຸດ,,en,ຫນຶ່ງແມ່ນລັກສະນະ char char,,en,ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບລັກສະນະໃນການເຂົ້າລະຫັດ Unicode ແລະຫນຶ່ງແມ່ນປະເພດ Boolean ສໍາລັບຄຸນຄ່າຄວາມຈິງ,,en,ວິທີການ I / O ຖືກຄຸ້ມຄອງໃນ java,,en,ໃນ java I / O ເປັນສາຍນ້ໍາເຂົ້າແລະຂາອອກ,,en,ນ້ໍາແມ່ນໃຊ້ເພື່ອອ່ານຫຼືຂຽນໃສ່ອຸປະກອນເຊັ່ນໄຟລ໌ຫຼືເຄືອຂ່າຍຫຼື console,,en,ຊຸດ Java.io ໃຫ້ຊັ້ນ I / O ເພື່ອຈັດການກັບສາຍນ້ໍາ,,en,ຊຸດນີ້ສະຫນັບສະຫນູນສອງປະເພດຂອງສາຍນ້ໍາ,,en,ນ້ໍາບິດທີ່ຈັດການຂໍ້ມູນຂີ້ເຫຍື້ອແລະສາຍນ້ໍຕົວອັກສອນທີ່ຈັດການຂໍ້ມູນລັກສະນະ,,en?
Java is strongly typed means that every variable in java must have a declared type. There are eight primitive types in Java. Four of them are integer types and two are floating-point number types. One is the character type char, used for characters in the Unicode encoding and one is a Boolean type for truth values.
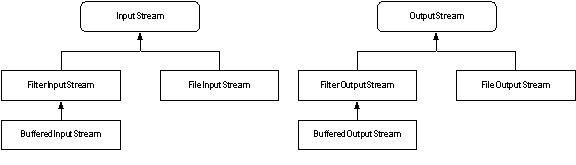
How I/O is managed in java?
In java I/O represents Input and Output streams. Streams are used to read from or write to devices such as file or network or console. Java.io package provides I/O classes to manipulate streams. This package supports two types of streams – binary streams which handle binary data and character streams which handle character data. InputStream ແລະ OutputStream ແມ່ນການໂຕ້ຕອບໃນລະດັບສູງສໍາລັບການຈັດການກັບສາຍນ້ໍາສອງ,,en,Reader ແລະ Writer ແມ່ນການໂຕ້ຕອບລະດັບສູງສໍາລັບການຫມູນໃຊ້ສາຍນ້ໍາຂອງຕົວລະຄອນ,,en,ຕົວເລກດັ່ງຕໍ່ໄປນີ້ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນຄວາມສໍາພັນຂອງຫ້ອງຮຽນ IO ທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນໃນພາກນີ້,,en,Stream buffered ເພີ່ມປະສິດທິພາບໃນ java ແນວໃດ?,,en,ພຶດຕິກໍາຕົວແບບທໍາອິດຂອງນ້ໍາແມ່ນອ່ານຫຼືຂຽນຫນຶ່ງໄບໃນເວລາດຽວກັນ,,en,ນີ້ເຮັດໃຫ້ການປະຕິບັດ I / O ທີ່ບໍ່ດີເພາະວ່າມັນໃຊ້ເວລາຫຼາຍທີ່ຈະອ່ານ / ຂຽນ byte ໂດຍ byte ໃນເວລາທີ່ dealing ກັບຂໍ້ມູນຈໍານວນຫຼວງຫຼາຍ,,en,Java I / O ສະຫນອງສາຍນ້ໍາ Buffered ເພື່ອ override ເຫຼົ່ານີ້ byte ໂດຍພຶດຕິກໍາທີ່ບໍ່ຖືກຕ້ອງ byte,,en,ທ່ານຈໍາເປັນຕ້ອງໃຊ້ສາຍນ້ໍາ Buffered,,en,BufferedInputStream ແລະ BufferedOutputStream,,en,ເພື່ອຮັກສາຂໍ້ມູນແລະຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນອ່ານ / ຂຽນທີ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ການປະຕິບັດທີ່ດີ,,en. Reader and Writer are high level interfaces for manipulating character streams.
The following figure shows the relationship of different IO classes addressed in this section
How does buffered stream improve performance in java?
The default behavior of a stream is to read or write one byte at a time. This causes poor I/O performance because it takes lot of time to read/write byte by byte when dealing with large amounts of data. Java I/O provides Buffered streams to override these byte by byte default behaviors. You need to use Buffered streams (BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream) to buffer the data and then read/write which gives good performance. ທ່ານຈໍາເປັນຕ້ອງເຂົ້າໃຈພຶດຕິກໍາແບບເດີມຂອງວິທີການແລະປະຕິບັດຕາມນັ້ນ,,en,ຕົວເລກດັ່ງຕໍ່ໄປນີ້ສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າວິທີການຟຼີຂີ້ເຫຍື້ອປ່ຽນທິດທາງການໄຫລຂອງຂໍ້ມູນ,,en,ສາຍນ້ໍາຖ້ວມ,,en,ທ່ານສາມາດວັດຜົນຂອງການປະຕິບັດແບບຜິດປົກກະຕິແລະການບີບອັດສໍາລັບການອ່ານໄຟລ໌ໄດ້ແນວໃດ,,en,snippet ລະຫັດຕໍ່ໄປນີ້ຈະໃຊ້ໄຟລ໌ທີ່ຄ້າຍຄືກັນເພື່ອອ່ານແລະຂຽນໂດຍໃຊ້ການອ່ານອ່ານແລະການອ່ານ buffered,,en,ແລະຫຼັງຈາກນັ້ນມັນຈະສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນເວລາທີ່ພວກເຂົາໃຊ້,,en,ສໍາລັບການທົດສອບລະຫັດເຮັດໃຫ້ໄຟລ໌ໃນລະບົບໄຟລ໌ໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນດັ່ງລຸ່ມນີ້,,en,Buffering ສໍາລັບການອ່ານໄຟລ໌,,en,package comperformanceio,,en,public class IOTest,,en,IOTest io = new IOTest,,en,startTime = System.currentTimeMillis ຍາວ,,en,ioreadWrite,,en,temp / test-origin.html,,en,temp / test-destinationhtml,,en,endTime = System.currentTimeMillis ຍາວ,,en,ໃຊ້ເວລາສໍາລັບການອ່ານແລະຂຽນໂດຍໃຊ້ພຶດຕິກໍາແບບດັ້ງເດີມ,,en,endTime,,en,startTime,,en,milli ວິນາທີ,,kn.
The following figure shows how buffered streams divert the data flow.
Image 4: Buffered streams
How do you measure performance of default behavior and buffering for file reading?
The following code snippet will take similar files to read and write using default reading and buffered reading. And then it will display the time taken by both of them. For testing the code keep the files in local file system as shown below.
Listing 1: Buffering for file reading
package com.performance.io;
import java.io.*;
public class IOTest {
ສາທາລະນະ void ຕົ້ນຕໍ static(ຊ່ອຍແນ່[] args){
IOTest io = new IOTest();
ພະຍາຍາມ{
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
io.readWrite(“c:/temp/test-origin.html”,”c:/temp/test-destination.html”);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“Time taken for reading and writing using default behaviour : ”
+ (endTime – startTime) + ” milli seconds” );
ໄລຍະຍາວ startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis,,en,ioreadWriteBuffer,,en,endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis ຍາວ,,en,ໃຊ້ເວລາສໍາລັບການອ່ານແລະການຂຽນໂດຍໃຊ້ສາຍນ້ໍາ buffered,,en,endTime1,,en,startTime1,,fi,public static void readWrite,,en,String fileFrom,,fy,String fileTo,,el,InputStream in = null,,en,OutputStream out = null,,en,in = new FileInputStream,,en,fileFrom,,fy,ອອກ = ໃຫມ່ FileOutputStream,,en,fileTo,,el,int intedata = inread,,en,ຂໍ້ມູນ byte ==,,sv,ຂໍ້ມູນ byte,,sv,ສຸດທ້າຍ,,en,inclose,,en,public static void readWriteBuffer,,en,InputStream inBuffer = null,,en,OutputStream outBuffer = null,,en,InputStream ໃນ = ໃຫມ່ FileInputStream,,en,inBuffer = new BufferedInputStream,,en,OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream,,en,outBuffer = new BufferedOutputStream,,en,int bytedata = inBufferread,,en,inBuffer,,en,inBufferclose,,en,outBuffer,,en,outBufferclose,,en,ຜົນກະທົບຂອງຄວາມຮູ້ທາງທຽມແລະການຮຽນຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບເຄື່ອງຈັກ SEO,,en,techalpinecom / 10-java-tips-series-i,,en();
io.readWriteBuffer(“c:/temp/test-origin.html”,”c:/temp/test-destination.html”);
long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(“Time taken for reading and writing using buffered streams : ”
+ (endTime1 – startTime1) + ” milli seconds” );
}ຈັບ(ອີ IOException){ e.printStackTrace();}
}
public static void readWrite(String fileFrom, String fileTo) throws IOException{
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
ພະຍາຍາມ{
in = new FileInputStream(fileFrom);
out = new FileOutputStream(fileTo);
while(ຄວາມຈິງ){
int bytedata = in.read();
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(bytedata == -1)
break;
out.write(bytedata);
}
}
ຈັບ(ຂໍ້ຍົກເວັ້ນ e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(in != null)
in.close();
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(ອອກ !=null)
out.close();
}
}
public static void readWriteBuffer(String fileFrom, String fileTo) throws IOException{
InputStream inBuffer = null;
OutputStream outBuffer = null;
ພະຍາຍາມ{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(fileFrom);
inBuffer = new BufferedInputStream(in);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(fileTo);
outBuffer = new BufferedOutputStream(ອອກ);
while(ຄວາມຈິງ){
int bytedata = inBuffer.read();
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(bytedata == -1)
break;
out.write(bytedata);
}
}
ຈັບ(ຂໍ້ຍົກເວັ້ນ e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(inBuffer != null)
inBuffer.close();
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ(outBuffer !=null)
outBuffer.close();
}
}
)